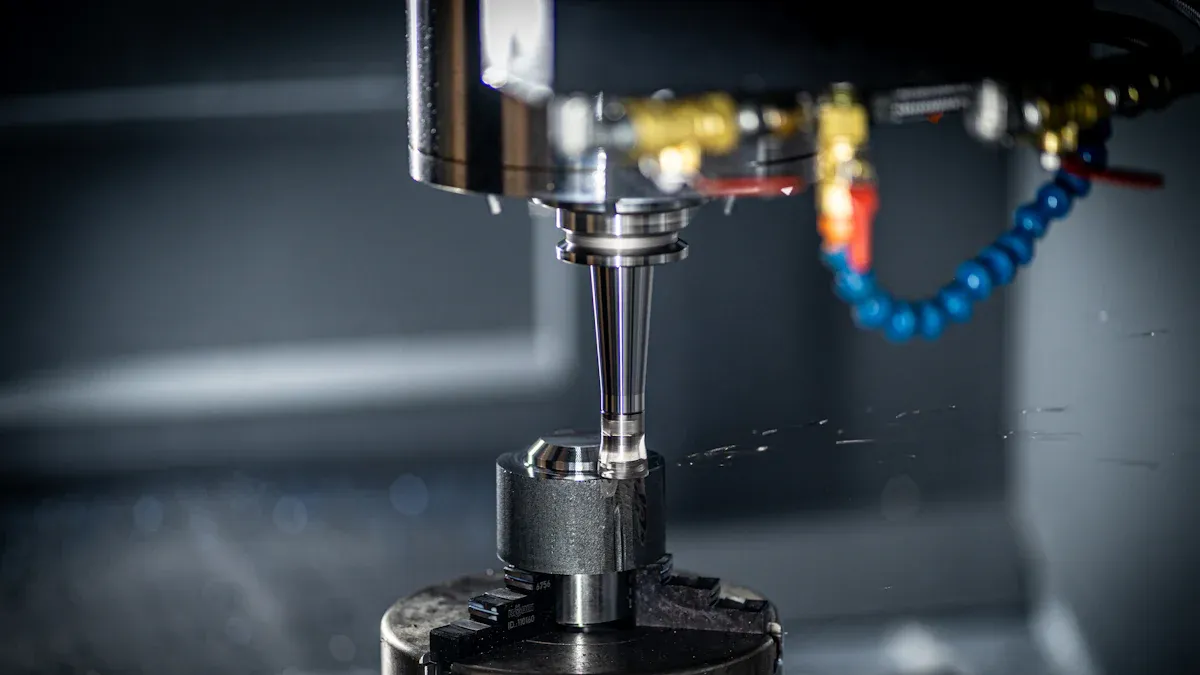

High-volume production requires the continuous and efficient manufacturing of many identical parts. Multi-spindle and Swiss-type CNC Turning Centers often provide the most effective solutions for these demanding production environments. These advanced machines ensure consistent Lathe Machine Precision and facilitate rapid output. Achieving optimal Precision CNC Machining at scale demands careful consideration of each machine’s capabilities. Industrial CNC lathe suppliers in China offer various options for different high-volume needs. Evaluating the CNC turning center price performance ratio becomes crucial for long-term success in such operations.
Key Takeaways
- Multi-spindle CNC machines make many simple parts fast. They work on several parts at the same time.
- Swiss-type CNC machines are best for small, complex parts. They make these parts very accurately.
- Automation helps CNC machines work without stopping. This includes robots and bar feeders.
- Good tools and regular machine care keep production smooth. They also save money.
- Choose a CNC machine based on your part’s size and how many you need. Also, think about the cost.
Multi-Spindle CNC Turning Centers for High-Volume Efficiency
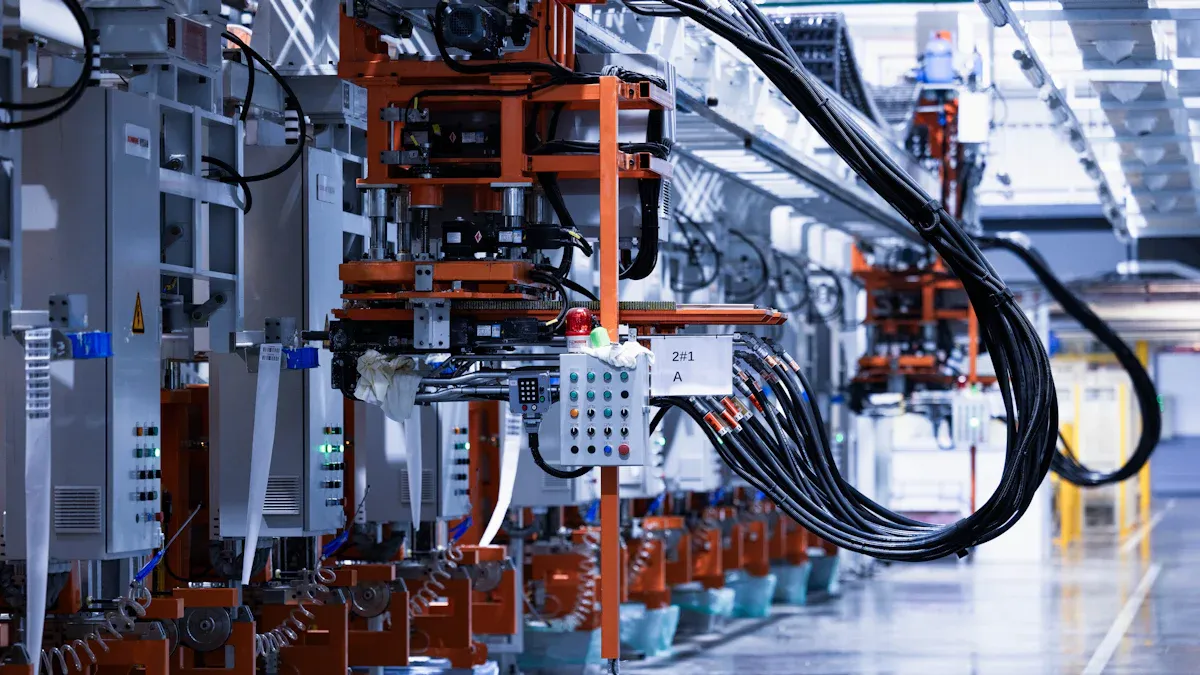
Simultaneous Machining Operations
Multi-spindle CNC turning centers are engineered for peak efficiency. They perform multiple machining operations simultaneously on several parts. These machines often utilize a combination of 6 main spindles and synchronous secondary spindles. This setup allows them to execute various tasks at once. They feature live tooling, automatic bar loading, and up to 26 axes of movement. This configuration rapidly produces finished parts. Some advanced models, like fully configurable INDEX CNC Multi-Spindle Turning Centers, offer 6 main spindles plus one swiveling synchronous spindle and up to 48-axis movement. This provides maximum machining versatility.
These machines also include a counter-spindle with a C-axis and a rework unit. This enables numerous counter-operations, avoiding additional handling. Operators can program a different speed for each spindle. This ensures optimal cutting conditions and exceptional surface quality. Multiple machining operations occur concurrently on several parts installed on different spindles within a single machine barrel. A symmetrical 2-spindle / 2-turret structure allows simultaneous machining on both spindles. Automatic transfer from the first to the second spindle ensures continuous operations. An automatic partition allows independent machining in both areas. One workpiece can be machined while another is replaced. Multi-axis CNC turning centers perform a wide array of operations, including simultaneous turning, milling, drilling, and tapping.
Reduced Cycle Times and Throughput
The ability to perform multiple operations at once dramatically reduces the cycle time per part. This simultaneous processing means a machine completes a part much faster than a single-spindle machine. The result is significantly increased throughput. Manufacturers can produce a higher volume of parts in less time. This efficiency directly translates into greater productivity and lower per-part costs for high-volume production runs.
Ideal Applications for Multi-Spindle CNC Turning Centers
Multi-spindle CNC turning centers excel in high-volume production across various industries. They are well-suited for:
- Automotive
- Hydraulics
- Plumbing
- Construction
- Agriculture
- Defense
- Medical & Pharmaceutical
- Data Centers
These machines accommodate bar stock sizes up to 51mm (2 inches) in diameter. They process a wide range of materials. This includes aluminum, stainless steel, and exotic metals. This versatility makes them ideal for diverse product types requiring consistent, high-volume output. Choosing the right CNC Turning Center for these applications ensures optimal production.
Swiss-Type CNC Turning Centers for High-Volume Precision
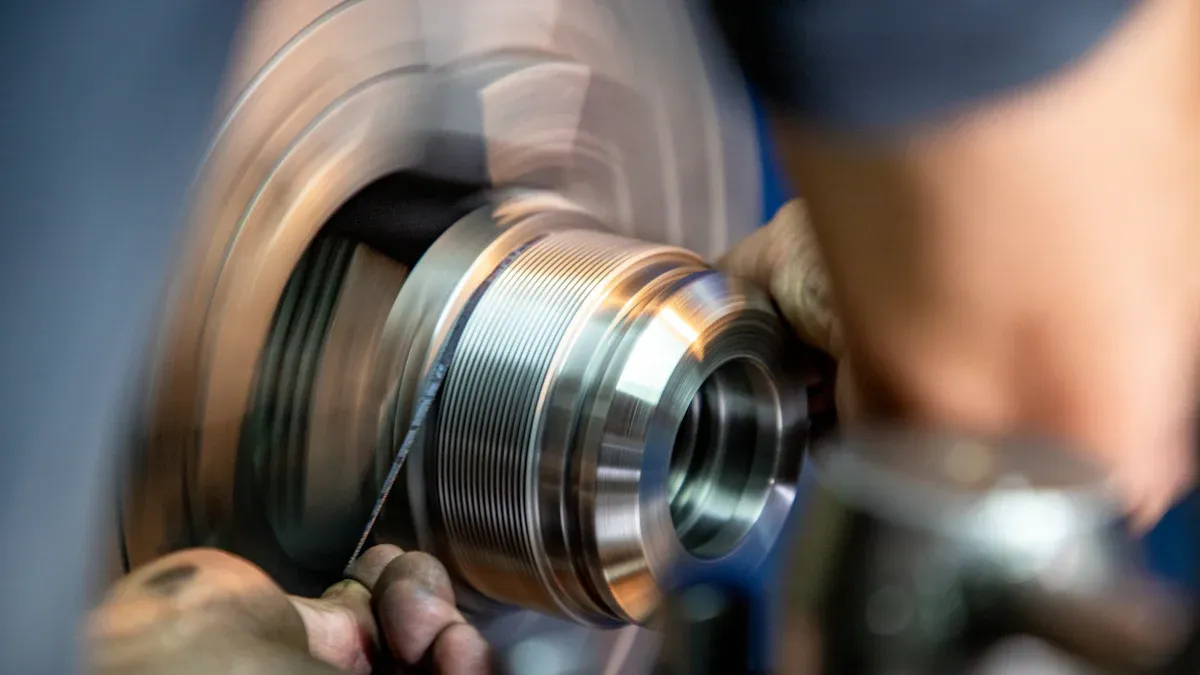

Sliding Headstock Mechanism for Accuracy
Swiss-type CNC turning centers are renowned for their exceptional precision, largely due to their unique sliding headstock mechanism. This design moves the bar stock through a guide bushing, allowing Z-axis movement. Only the portion undergoing machining remains exposed, while the cutting tool stays stationary. This method significantly minimizes part deflection. It enables manufacturers to achieve tight tolerances, especially for long workpieces and small diameters. The sliding headstock and guide bushing system effectively reduce vibration and deflection. This setup allows for exceptionally accurate and tight-tolerance machining, particularly for small-diameter parts. The guide bushing offers crucial support, reducing flex and enhancing stability during machining. This design is particularly advantageous for small-diameter parts by minimizing deflection and improving stability. The close proximity of the cutting tool to the guide bushing ensures precise and accurate turning operations for intricate and complex components.
Benefits for Long, Slender Parts
Swiss CNC lathes significantly enhance stability, allowing for the machining of delicate parts with precise tolerances at high speeds. The machine design provides firm support directly adjacent to the cutting point, keeping parts steady and unaffected by tool force. This enables the machine to maintain precision even when machining tiny parts within extremely tight tolerances. The stable and supportive bar stock, combined with various tooling, facilitates the creation of more delicate and intricate pieces. This includes thin walls with deep cuts, which pose challenges for traditional lathes. Swiss CNC machines feed bar stock through a guide bushing, holding the material firmly in place close to the machining operation. This method significantly increases stability and precision by preventing deformation and flexing of the workpiece. This in turn reduces errors and leads to tighter tolerances on finished parts. This capability is particularly crucial for delicate or slender components that are difficult to machine using conventional methods.
High-Volume Production of Complex Small Parts
Swiss-type CNC turning centers excel at the high-volume production of complex small parts across various industries. Their precision and stability make them ideal for components requiring intricate features and tight tolerances. Common applications include:
- Oil Field Services: High-pressure valve parts, downhole tool parts, precision sensor housings, and hydraulic fittings.
- Aerospace: Fuel system components, pneumatic/hydraulic fittings, electrical connectors, fasteners, and pins.
- Defense: Firing pin components, optical system housings, parts of telecommunication devices, and precision mechanical assemblies.
- Telecommunications: Connector components, waveguide parts, antenna elements, and high-precision cases for electronic components.
- General: Various types of threaded parts are also well-suited for these machines.
Comparing CNC Turning Centers: Multi-Spindle vs. Swiss-Type
Choosing between multi-spindle and Swiss-type CNC turning centers requires a detailed understanding of their strengths. Each machine excels in different high-volume production scenarios. Manufacturers must evaluate specific production needs to make the best decision.
Throughput and Part Complexity Considerations
Multi-spindle CNC turning centers are champions of high throughput. They perform multiple operations concurrently. This significantly reduces the time to complete each part. Dual-spindle CNC lathes, for example, cut down cycle times by working on both ends of a part simultaneously. This eliminates manual re-chucking and minimizes idle time. Such efficiency directly leads to higher production rates. These machines also handle increased part complexity. They machine both sides of a part without interruption. This opens new design possibilities for specialized components. Multi-spindle machines minimize part handling and setup. The second spindle often automatically takes the part from the first. This lowers labor costs and reduces human error.
| Feature | Single-Spindle CNC Turning Center | Dual-Spindle CNC Turning Center |
|---|---|---|
| Operations Performed | One operation at a time | Multiple operations simultaneously |
| Clamping and Repositioning | More time required | Reduced time, enhancing productivity |
| Processing Speed | Slower due to sequential tasks | Faster due to concurrent tasks |
| Flexibility for Complex Tasks | Limited | High flexibility with quick tool switching |
| Integration with Automation | Limited | High integration for unmanned operation |
Swiss-type CNC lathes, on the other hand, streamline operations for high-volume, single-axis parts. They excel with tight tolerances, often ±0.0001″. These machines are ideal for micro-machining components under 1.5″ in diameter. They support multi-directional machining for parts needing complex contours or irregular shapes. Swiss-type machines are designed for high-precision, small-diameter parts. They use multiple tools simultaneously in a single setup. For parts combining both turning and milling requirements, such as fuel injectors or hydraulic valves, multi-tasking machines offer a hybrid solution. These systems integrate Swiss lathe capabilities with live tooling and sub-spindles. They reduce setups and enhance accuracy for components demanding both rotational and milling operations.
Material Suitability and Tolerance Capabilities
Multi-spindle CNC turning centers process a wide range of materials effectively. These include steel, carbon steel, aluminum, brass, copper, and stainless steel. Steel and carbon steel are common for general machining. Finer materials like copper, brass, aluminum, and stainless steel are frequently used for specialty or high-precision parts. These materials often require specific physical properties, such as corrosion or wear resistance.
Swiss-type CNC turning centers are renowned for their extreme accuracy. They maintain tolerances of +/-.0002″. This precision comes from their design, which includes a precision bushing and a supporting, sliding headstock. This system minimizes deflection and vibration. It is particularly effective for manufacturing long parts with small diameters. Typical tolerance ranges for CNC Swiss Screw Machining are around +/-.0005” (+/-.013mm). These machines often feature 11-axis control, twin turrets, and 4-axis back working. They handle highly complex precision parts with both speed and accuracy. Specialized processes can achieve tolerances as tight as ±0.0001″ on specific features. This requires extensive process controls and may affect production costs.
| Machine Type | Typical Tolerance Range | Best-Case Tolerance |
|---|---|---|
| Swiss Lathe | ±0.0002″ to ±0.0005″ | ±0.0001″ |
Cost-Effectiveness for Different High-Volume Scenarios
The cost-effectiveness of multi-spindle versus Swiss-type CNC turning centers varies significantly. Swiss-type CNC turning centers typically have a higher initial investment. However, they often lead to lower per-part costs, especially for high-volume production of small, complex parts. Their efficiency is increased, and scrap rates are reduced due to their precision. Labor requirements are minimal because they often complete parts in a single setup.
Conventional CNC lathes, which can include multi-spindle machines, generally have a lower initial investment. However, their per-part costs can be higher for very high-volume production of complex parts. This is due to potentially longer cycle times or the need for secondary operations.
| Cost Factor | Swiss-type CNC Turning Centers (Swiss Lathes) | Conventional CNC Lathes (can include multi-spindle) |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Investment | Higher | Lower |
| Per-Part Costs | Lower (especially for high-volume production) | Higher (especially for high-volume production) |
| Efficiency | Increased | Lower (due to longer cycle times) |
| Scrap Rates | Reduced | Potential for higher |
| Labor Requirements | Minimal | Potentially higher (due to secondary operations) |
Manufacturers must weigh the initial capital outlay against long-term operational savings. The choice depends on the specific part geometry, material, required tolerances, and overall production volume.
Optimizing High-Volume CNC Turning Center Production
High-volume production demands continuous operation and maximum efficiency from CNC turning centers. Optimizing these machines involves strategic integration of automation, smart tooling choices, and robust maintenance practices. These elements work together to ensure consistent output and reduce operational costs.
Automation Integration with Robotics and Bar Feeders
Automation significantly boosts productivity in high-volume CNC turning. Bar feeders, like the Iemca ELITE-112, automatically supply raw material, ensuring uninterrupted production runs. This 12-foot system reduces manual intervention and minimizes downtime. Robotic systems, such as the Retriever 1700, handle secondary operations and robotic pick-and-place tasks. Solutions like Smart Bin alleviate challenges in robotic bin picking. Load and accumulation tables, like Corso 1955 and Corso 1925, organize and hold parts for machine tending, enabling hours of unattended runtime. Gantry loaders offer high-speed, high-precision workpiece replacement. Robotic cell systems, such as the Mazak AUTO FLEX CELL, provide autonomous operation for variable-mix, variable-volume production. These integrations allow continuous machine operation and reduce cycle times.
Tooling Optimization for Continuous Operation
Tooling optimization directly impacts continuous operation and cost-effectiveness. Investing in premium tooling, such as high-performance coated carbide tools, significantly extends tool life. These tools last 5-10 times longer, reducing the total cost per part despite a higher initial investment. Manufacturers minimize tool changes by designing operations to use the same tool for multiple features. They group similar operations and utilize multi-functional tools. This strategy saves considerable time per part. Implementing tool life management systems ensures proactive tool replacement before failure. These systems maintain consistent tool offset data and keep detailed performance records. This reduces crashes from worn tools and improves production consistency.
Maintenance Strategies for CNC Turning Centers
Effective maintenance strategies are crucial for high uptime and accuracy. Preventative maintenance transforms random failures into predictable work windows. Daily tasks include checking lubricant and coolant levels and cleaning the machine. Weekly checks involve inspecting cooling fans and looking for leaks. Monthly tasks include cleaning coolant tanks and replacing primary filters. Annual maintenance involves comprehensive control and drive system reviews. These regular checks detect wear, contamination, and misalignment early. This prevents minor issues from escalating into major machine-stopping events. A Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) or Maintenance Management System (MMS) integrates data from operators and maintenance staff. This system supports maintenance planning and intervention decisions, preserving CNC performance for production.
Selecting the Best CNC Turning Center for Your Needs
Choosing the optimal CNC turning center for high-volume production involves a careful evaluation of several critical factors. Manufacturers must consider part characteristics, production volume, investment costs, operational expenses, and future technological advancements. A strategic decision ensures long-term efficiency and profitability.
Part Characteristics and Production Volume
The specific characteristics of the parts a manufacturer produces heavily influence the choice of a CNC turning center. Part size, complexity, and the material used are primary considerations. For instance, a Swiss-type CNC turning center justifies its investment when producing a series of long, complex parts in high volumes. These machines excel at maintaining tight tolerances on slender components. Conversely, multi-spindle machines are suitable for high-volume jobs where cycle time is critical. They rapidly produce simpler, larger parts. Manufacturers must assess their specific production volume thresholds. This helps determine which machine type offers the most efficient output for their unique product line.
Investment and Operational Cost Analysis
A thorough financial analysis is essential before investing in a high-volume CNC turning solution. The upfront investment for a multi-spindle or Swiss-type CNC lathe typically ranges from $100,000 to over $300,000. This initial capital outlay represents a significant commitment.
| CNC Turning Center Type | Upfront Investment Cost |
|---|---|
| Multi-Spindle or Swiss-Type CNC Lathe | $100,000 – $300,000+ |
Beyond the initial purchase, operational costs significantly impact the total cost of ownership. Several factors contribute to these ongoing expenses. Labor costs are a major component, directly influenced by cycle time and machining time. Longer machining times increase both energy and labor costs per part. Energy costs also represent a substantial factor. Parasitic losses and inefficient designs contribute to higher consumption. Machine tool components like the cooling and lubrication system (31%), hydraulic system (27%), auxiliary systems (19%), and servo drives (17%) all consume energy. Idle consumption and standby modes also add to energy usage. Drive system and motor efficiency, machining parameters (cutting speed, feed rate, coolant discharge rate), and process planning and optimization directly affect energy consumption. Overhead costs, such as utilities, rent, insurance, administrative expenses, and taxes, are indirect but still link to machining operations. They influence overall costs. Other operational expenses include equipment costs, tooling costs, material costs, and inventory costs. Manufacturers must evaluate all these elements to determine the true cost-effectiveness of a CNC turning center.
Future-Proofing Your High-Volume CNC Turning Center
Preparing for future technological advancements ensures a CNC turning center remains competitive and efficient for years to come. The manufacturing landscape is rapidly evolving, driven by automation and smart manufacturing. This leads to increased demand for CNC machines integrated with AI, IoT, and robotics.
Several key advancements are anticipated:
- AI-powered vision systems will provide automated quality control. They will identify deviations immediately after machining.
- Integration of neural networks will enable CNC systems to learn from previous manufacturing runs. This optimizes cycle times and improves tool life by nearly 20%.
- New AI-based CNC controllers will use deep learning algorithms. They will predict optimal machining parameters in real-time. This enhances machining accuracy by up to 15% and significantly reduces setup times.
- Increased demand for multi-tasking CNC machines will combine milling, turning, drilling, and sometimes grinding functions into a single setup. This reduces production cycles by up0 to 30%.
- Integration of digital twin technology will create virtual replicas of machines and processes. This simulates machining operations, detects potential issues, and optimizes performance.
- Adoption of energy-efficient CNC systems will incorporate energy regeneration and more efficient motor designs. This reduces power consumption by nearly 18%.
A growing focus on lights-out manufacturing accelerates the demand for AI in the high-end CNC machine tool sector. Enhanced features like remote machine monitoring, real-time diagnostics, and adaptive controls are becoming standard. Manufacturers should prioritize machines capable of integrating these future technologies. This ensures their investment remains valuable and adaptable to evolving production demands.
Multi-spindle CNC turning centers excel in high-volume production of simpler, larger parts, delivering maximum throughput. Conversely, Swiss-type CNC turning centers prove superior for high-volume manufacturing of small, complex, and high-precision components. The ideal CNC Turning Center selection hinges on specific part characteristics, production volume demands, and available budget. Therefore, businesses must carefully evaluate their unique production needs to identify the most efficient and cost-effective solution.
FAQ
What is the primary distinction between multi-spindle and Swiss-type CNC turning centers?
Multi-spindle machines excel at high-volume production of simpler, larger parts. They perform simultaneous operations. Swiss-type machines specialize in high-precision, small, complex parts. They utilize a sliding headstock for accuracy.
Which CNC turning center is ideal for manufacturing small, intricate components?
Swiss-type CNC turning centers are ideal for small, intricate components. Their sliding headstock mechanism minimizes part deflection. This allows them to achieve tight tolerances on slender and complex parts.
Can multi-spindle CNC turning centers process a variety of materials?
Yes, multi-spindle CNC turning centers process a wide range of materials. These include steel, carbon steel, aluminum, brass, copper, and stainless steel. This versatility suits diverse product types.
How does automation enhance high-volume CNC turning production?
Automation, through bar feeders and robotics, ensures continuous operation. It reduces manual intervention and minimizes downtime. This significantly boosts productivity and allows for unattended production runs.
What key factors should guide the selection of a CNC turning center for high-volume needs?
Manufacturers should consider part characteristics, production volume, and investment costs. They also need to analyze operational expenses and future technological integration. This ensures an efficient and profitable long-term solution.
Post time: Feb-05-2026







