
Modern CNC Turning Centers integrate advanced automation, enhanced precision, and intelligent connectivity. These innovations deliver unparalleled efficiency, accuracy, and versatility in manufacturing. The High Speed CNC Turning Center Market projects a 5.8% Compound Annual Growth Rate from 2025 to 2035, underscoring the increasing demand for these sophisticated machines. A Multi-Function CNC Lathe Manufacturer continually develops such High Precision Lathe systems. This ensures superior Precision Machining capabilities. An advanced CNC Control System is central to these modern functionalities.
Key Takeaways
- Modern CNC turning centers use strong parts and special systems to stop shaking. This helps them make very exact parts.
- These machines work faster with robots and special tools. They can make complex shapes in one step.
- Modern CNC machines connect to the internet. This helps them check their own parts and fix problems before they happen.
- New CNC machines save energy and are safer for workers. They have features that protect people and the environment.
The Foundation of Precision in a Modern CNC Turning Center

High-Rigidity Machine Structure and Damping Systems
Modern CNC turning centers prioritize structural integrity. They feature robust machine beds and components. This design minimizes vibration and deflection during machining. Advanced damping systems further enhance stability. These systems actively absorb unwanted oscillations. In unstable cutting, they reduce root-mean-square vibration levels by over 95%. Peak-to-peak values see approximately a 90% reduction. Even in stable cutting, reductions range from 10% to 50%. Such stability ensures consistent part quality and extends tool life.
Direct Drive Spindles and High-Resolution Encoders for CNC Turning Centers
Modern CNC turning centers use direct drive spindles. These eliminate belts and gears. This design reduces mechanical losses and backlash. Two common types exist: direct-drive spindles and built-in motor spindles. Direct-drive spindles connect the rotor directly to the motor’s stator. They offer precise speed control and quick acceleration. They have low maintenance needs. However, they provide lower torque at low speeds. Built-in motor spindles integrate the motor’s rotor inside the spindle shaft. They achieve ultra-high speeds, often exceeding 40,000-60,000 rpm. They offer superior precision and balance. These spindles require efficient cooling.
High-resolution encoders complement these spindles. They provide extremely accurate position feedback. For precision CNC, resolutions typically range from 0.1 to 1 μm. Some absolute encoders measure positions as fine as 1 nm. Optical encoders, like the ENX 16 RIO, achieve up to 65,536 counts per turn. High count per turn values ensure highly constant velocity control.
Advanced CNC Control Systems for Modern Turning Operations
Advanced CNC control systems form the brain of modern turning operations. They process complex machining programs rapidly. These systems offer sophisticated algorithms for tool path optimization. They manage multi-axis movements with high synchronization. Real-time data processing ensures dynamic adjustments during cutting. Operators benefit from intuitive interfaces. These controls support advanced features like collision avoidance. They also enable adaptive control, which adjusts parameters based on cutting conditions. This leads to higher material removal rates and improved surface finishes.
Boosting Productivity with Modern CNC Turning Center Automation

Integrated Automation: Robotics and Gantry Loaders
Modern manufacturing significantly boosts productivity through integrated automation. Robotics play a crucial role in machine tending and material handling. Manufacturers utilize various robot types for these tasks. For example, Fanuc M-10 Series robots offer compact designs and precise repeatability for machine tending. ABB IRB 2600 robots excel in high-speed material handling. Collaborative robots, like the Universal Robots UR Series, safely interact with human operators. Halter CNC Automation’s LoadAssistant provides seamless integration for robot loading.
Different robot types serve specific functions:
| Type of CNC Robot | Key Features | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| SCARA Robots | High-speed horizontal motion, 4-axis structure | Assembly, material handling |
| Articulated Robots | Multiple joints (6+ axes), high flexibility | Cutting, welding, complex trajectory machining |
| Cartesian (Gantry) Robots | Linear movement in X/Y/Z axes, high rigidity | Large workpiece handling, drilling |
| Collaborative Robots (Cobots) | Safe human-robot collaboration, simple programming | Machine tending, quality inspection |
Gantry loaders further enhance automation. They reduce overall cycle times by 20-30 percent in most applications. This efficiency comes from parallel processing. The robot loads the next part while the machine finishes the current one.
Multi-Axis Machining and Y-Axis Functionality in CNC Turning Centers
Multi-axis machining capabilities are essential for modern productivity. They allow the creation of complex geometries and intricate designs. This includes precise 3D shapes and hard-to-reach areas. Multi-axis machines also improve surface finish by reducing tool marks. They offer versatility for various materials and part sizes.
Live tooling, combined with Y-axis and C-axis control, expands machining possibilities. The C-axis rotates the workpiece to exact angles. The Y-axis moves tools above and below the part’s centerline. These features enable off-center drilling, non-cylindrical contours like keyways, and advanced threading. Such capabilities lead to higher precision and faster production speeds. They also reduce the number of setups required. Industries like aerospace, automotive, and medical devices benefit greatly from Y-axis functionality. It allows for complex parts with intricate geometries in a single setup. This is crucial for milling slots and pockets across a part’s face, ensuring perpendicular walls.
Live Tooling and Automatic Tool Changers for CNC Turning Centers
Live tooling transforms a standard lathe into a multi-tasking machine. It allows powered tools on the turret to rotate independently. This enables operations like drilling perpendicular holes, milling flat features, and tapping threads in one cycle. Common types of live tooling include:
- Live Tool Spindles for multi-axis cutting.
- Live Tool Extensions to reach intricate areas.
- Live Tool Coolant Systems for improved performance.
- Rotary Tables and Indexers for precise workpiece rotation.
Automatic tool changers complement live tooling. They switch between different tools rapidly. The typical tool exchange time is just a few seconds. This rapid change significantly enhances the continuity and efficiency of the machining cycle in a modern CNC Turning Center.
Smart Factory Connectivity for the Modern CNC Turning Center
IoT and Industry 4.0 Readiness for CNC Turning Centers
Modern CNC turning centers embrace IoT and Industry 4.0 principles. This integration allows for real-time monitoring of machine status, spindle load, and tool wear. It enables predictive maintenance, scheduling service before breakdowns occur. Manufacturers achieve higher productivity and automation through continuous, unattended production. Data-driven decision-making provides actionable insights for throughput, quality, and capacity planning. These systems also offer customization and flexibility, allowing quick changeovers and efficient small batch production. Automated job scheduling, tool life management, and energy efficiency tracking further enhance operations. Remote machine diagnostics and higher precision, especially with 5-axis machining, improve overall performance. This leads to increased operational efficiency and greater profitability.
Integrated Sensors for Process Monitoring and Predictive Maintenance
Integrated sensors are vital for process monitoring and predictive maintenance. Vibration sensors detect machine vibrations, while strain sensors measure force. Power sensors, like the PT800 Power Transducer, monitor 3-phase power load on the tool to determine wear. Thermocouple and infrared sensors monitor the temperature of key components such as the spindle and guideways. Accelerometers detect vibration frequency and amplitude along X/Y/Z axes. Acoustic sensors analyze cutting noise for anomalies like tool chipping. Wear sensors, such as laser displacement sensors, detect changes in tool tip radius. Pressure sensors monitor clamping force and hydraulic systems. These sensors provide crucial data, enabling machines to predict maintenance needs and prevent unexpected downtime.
User-Friendly HMI and Programming Interfaces for CNC Turning Centers
User-friendly Human-Machine Interfaces (HMI) are essential for modern CNC turning centers. They feature intuitive user interfaces with logical layouts and clear icons, minimizing training needs. High-resolution touchscreens are robust and responsive, allowing operators to read information from a distance. Customizable dashboards let operators personalize their display to show relevant data, like spindle metrics. Advanced data visualization uses graphs and charts to present complex data, such as tool paths or real-time spindle load. Seamless connectivity integrates with factory systems for data logging and remote monitoring. This design reduces cognitive load and prevents inadvertent critical actions.
Programming interfaces commonly use G-code and M-code. Operators can program manually, directly at the machine with graphical user interfaces, or through CAD/CAM systems. ISO programming language is an international standard for controlling machine motion. Custom macro programs enhance programming efficiency through modularity. High-level languages offer more flexible and complex machine programming.
Operational Considerations for a Modern CNC Turning Center
Energy Efficiency and Reduced Environmental Impact
Modern manufacturing prioritizes energy efficiency and environmental responsibility. Modern machines significantly reduce energy consumption compared to older models. These advancements lead to substantial savings and a smaller carbon footprint.
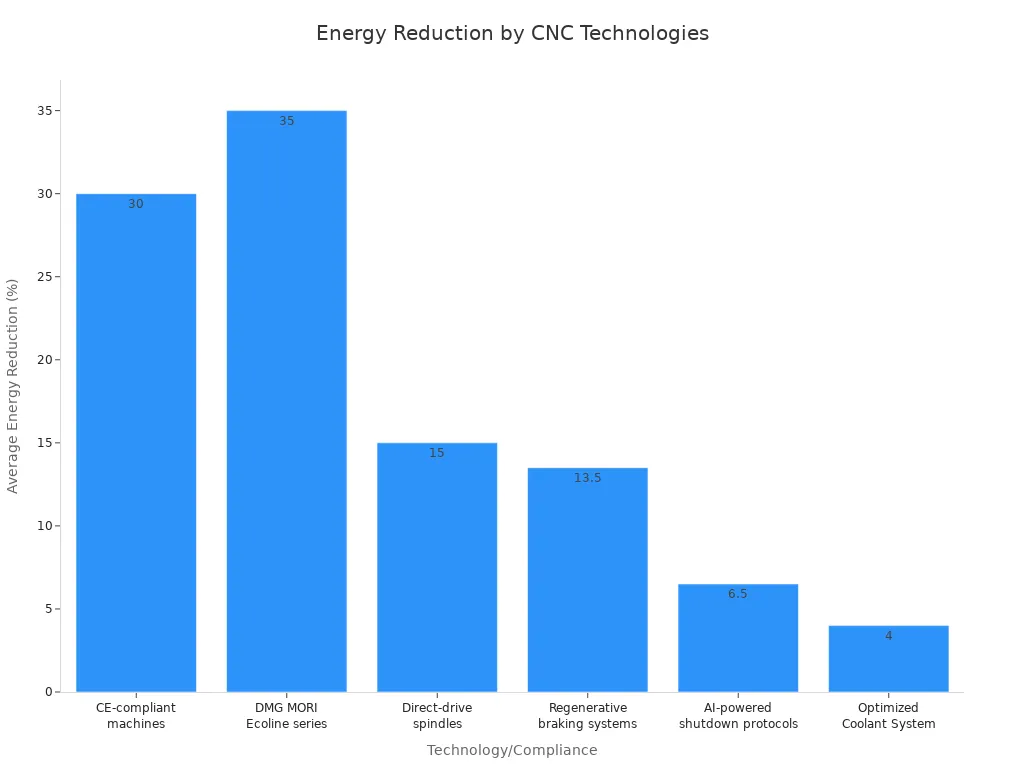
Several technologies contribute to these reductions:
| Technology/Compliance | Energy Reduction/Savings |
|---|---|
| CE-compliant machines (vs. older models) | 25-35% lower energy bills |
| DMG MORI Ecoline series (average) | 35% reduction in power consumption |
| Direct-drive spindles | 15% energy savings |
| Regenerative braking systems | 12-15% energy recovery |
| AI-powered shutdown protocols | 5-8% smart shutdown |
| Optimized Coolant System | 3-5% Reduction |
Predictive maintenance uses sensors and data analytics. It anticipates equipment failures, preventing downtime and reducing waste from defective products. Real-time monitoring allows immediate adjustments to machining processes. This optimizes efficiency and minimizes resource consumption. Artificial intelligence (AI) integration analyzes data. It identifies patterns and recommends process improvements for more sustainable operations. Upgrading to energy-efficient machinery incorporates features like variable frequency drives. Intelligent power management systems reduce electricity consumption. Optimizing machining processes uses software. It optimizes tool paths and machining parameters, decreasing cycle times and energy usage. Implementing renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power, further reduces the carbon footprint. Enhanced automation integrates AI and machine learning. It optimizes machining processes, reduces material waste through precise cuts, and extends tool lifespan. Recycling and closed-loop systems promote a circular economy. They reuse byproducts and minimize waste.
Ergonomic Design and Advanced Safety Features
Ergonomic design improves operator comfort and reduces fatigue. This leads to higher productivity and fewer errors. Advanced safety features protect personnel and equipment. They ensure a secure working environment.
Modern machines include several critical safety components:
- Emergency Stop Buttons: Strategically placed buttons immediately halt operations during malfunctions or errors.
- Interlocking Guards: Mechanical or electronic devices prevent access to hazardous areas. They stop the machine if tampered with.
- Automatic Tool Measurement and Monitoring: These systems reduce tool failure or breakage. Tool failure can pose a significant hazard at high speeds.
- Mist Collection and Filtration Systems: These systems collect hazardous mists and metal particles generated during operations. They improve air quality.
- Collision Detection Systems: Sensors and software stop machine operations upon detecting potential collisions. This minimizes damage and safety risks.
- Automatic Shutdown for Overloads: Features automatically shut down operations when abnormal stress or overheating occurs. This prevents fires and safeguards operators.
- Training and Software Limitations: Software controls limit operational speed and functions based on user access and competence. This ensures unskilled operators work within safe limits.
- Real-Time Monitoring Systems: IoT-enabled systems provide live updates on machine health and operational parameters. This allows for proactive prevention of accidents.
A truly modern CNC Turning Center integrates advanced mechanics, intelligent automation, and smart connectivity. This synergistic combination defines its capabilities. Investing in these key features ensures future-proof manufacturing capabilities. It delivers superior precision, efficiency, and adaptability for various production needs. Manufacturers achieve optimal performance and sustained competitiveness with these advanced systems.
FAQ
What defines a modern CNC turning center’s precision?
Modern centers achieve precision through high-rigidity structures and advanced damping systems. They incorporate direct-drive spindles and high-resolution encoders. These components minimize vibration and ensure extremely accurate position feedback. This design guarantees consistent part quality.
How do modern CNC turning centers boost productivity?
They boost productivity through integrated automation, including robotics and gantry loaders. Multi-axis machining with Y-axis functionality allows complex part creation in one setup. Live tooling and automatic tool changers further reduce cycle times and enhance versatility.
What role does IoT play in modern CNC turning centers?
IoT enables real-time monitoring of machine status and tool wear. It facilitates predictive maintenance and data-driven decision-making. This connectivity supports continuous, unattended production and optimizes operational efficiency. It also allows remote diagnostics.
What are the main benefits of investing in a modern CNC turning center?
Investing in a modern CNC turning center ensures superior precision, efficiency, and adaptability. It provides future-proof manufacturing capabilities. These machines deliver higher material removal rates, improved surface finishes, and reduced operational costs. They also enhance overall competitiveness.
Post time: Dec-11-2025







