
Choosing the right Cnc Machining Center in 2025 is vital for business efficiency, productivity, and profitability. This strategic decision requires careful evaluation. The 4-axis CNC Machining Center market anticipates a 5.9% Compound Annual Growth Rate from 2025 to 2032, indicating significant opportunity. Similarly, the market for a Vertical Machining Center projects 5% annual growth. This guide helps businesses understand essential considerations, from operational needs to advanced features and return on investment. Businesses might also explore a Cnc Turning Center, a Horizontal Cnc Lathe Machine, or a high-precision 5 Axis Vertical Machining Center to meet specific production demands.
Key Takeaways
- Understand your business needs first. Look at how much you make, what materials you use, and how complex your parts are. This helps you pick the right machine.
- Explore different types of CNC machines. Vertical, horizontal, 5-axis, and multi-tasking machines each have special uses. Choose the one that fits your production best.
- Look for key features and new technology. Check spindle speed, tool changer capacity, and the control system. Also, consider automation, robotics, and how well the machine connects to other systems.
- Think about the total cost, not just the price. Include operating costs, maintenance, and how much the machine will be worth later. This helps you see the real value over time.
- Choose a good vendor. They should have a strong reputation, offer good support and training, and provide a solid warranty. This ensures you have help when you need it.
Understanding Your Business Needs for a CNC Machining Center in 2025
Businesses must thoroughly assess their operational requirements before investing in a new Cnc Machining Center. This crucial step ensures the chosen equipment aligns perfectly with production goals and financial realities. A clear understanding of current and future needs prevents costly missteps and maximizes the return on investment.
Current and Projected Production Volume
Evaluating production volume is fundamental. It dictates the machine’s required capacity and speed. Businesses should consider both their current output and anticipated growth. Different manufacturing scales demand different machine capabilities.
| Manufacturing Scale | Production Volume (Units per Year) |
|---|---|
| Small/Batch Production | 100 – 10,000 |
| Higher-Volume/Mass Production | 10,000 or more |
This assessment helps determine if a single machine suffices or if multiple units are necessary.
Material Types and Part Complexity
The types of materials a business processes and the complexity of its parts significantly influence machine selection. CNC machining centers handle a wide range of materials, including various metals, plastics, and composites. Each material possesses unique properties and machining requirements.
- CNC machining centers process various materials, including metals, plastics, and composites.
- Material selection depends on environmental conditions, thermal exposure, conductivity, mechanical loading, surface finish, aesthetics, cost, weight, and manufacturing method.
- Specific materials include stainless steel (grades 304, 316, 416, 17-4 PH), brass (360 Brass), alloy steel (4130, 4140), carbon steel (1018, 1045), rigid foam, carving foam, phenolics (G7, G11, G9, G10/FR4, G10, LE, CE), and various plastics (HDPE, Nylon, PEEK, Polycarbonate).
- Harder materials require more wear-resistant tools and finer machining parameters.
- Metallic materials often need coolant to prevent overheating and deformation.
Complex geometries may necessitate multi-axis capabilities.
Budgetary Constraints and Financial Planning
Financial planning forms a critical part of the decision-making process. Businesses must establish a realistic budget for the acquisition. The cost of CNC machines varies widely based on type and capabilities.
| Machine Type | Entry-level (Price Range) | Mid-range (Price Range) | High-end (Price Range) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNC Milling Machines | $10,000 – $30,000 | $30,000 – $100,000 | $100,000 – $500,000 |
| CNC Lathe Machines | $10,000 – $30,000 | $30,000 – $100,000 | $100,000 – $500,000 |
| CNC Router Machines | $5,000 – $20,000 | $20,000 – $75,000 | $75,000 – $200,000 |
| CNC Plasma Cutting | $10,000 – $30,000 | $30,000 – $100,000 | $100,000 – $500,000 |
| CNC Laser Cutting | $20,000 – $50,000 | $50,000 – $200,000 | $200,000 or more |
Beyond the initial purchase price, businesses must account for installation, training, maintenance, and operational costs. A comprehensive financial plan ensures long-term viability.
Space and Infrastructure Requirements
Businesses must carefully assess their available physical space before acquiring new machinery. A machine’s footprint is a primary consideration. However, companies also need to account for additional clearance. This includes space for operators, material handling, and routine maintenance access. Future expansion plans should also influence this assessment. Inadequate space can severely limit production capacity and hinder future growth.
Different Vertical Machining Center (VMC) models have varying space requirements. The following table illustrates typical floor space needs for several VMC models:
| VMC Model | Floor Space Requirements (L x W) |
|---|---|
| VMC 1000B | 900 x 2090mm |
| VMC 1200B | 3600 x 2244mm |
| VMC 1500B | 4400 x 2244mm |
| VMC 1600B | 4520 x 2244mm |
| VMC 1000L | 2900 x 2090mm |
| VMC 1200L | 3398 x 2221mm |
| VMC 1300L | 3650 x 2220mm |
Beyond the physical footprint, infrastructure requirements are equally important. Adequate electrical power supply is essential. Machines often demand specific voltage and amperage. Companies must verify their existing electrical systems can support the new equipment. An insufficient power supply can lead to machine malfunctions or reduced performance.
Compressed air is another common requirement for many machining operations. This includes tool changes, chip removal, and pneumatic clamping. Businesses need to ensure a reliable and sufficient compressed air supply. Proper ventilation systems are also crucial. They manage heat and remove airborne particles. This maintains a safe and healthy working environment for personnel. Some advanced machines may also require dedicated cooling systems to maintain optimal operating temperatures.
Finally, the foundation supporting the machine needs evaluation. Heavy machinery requires a stable and level base. This prevents vibrations and ensures machining precision. An unstable foundation can compromise part accuracy and machine longevity. Consulting with machine manufacturers or structural engineers can help determine specific foundation needs. Proper planning for space and infrastructure prevents installation delays and operational issues. It ensures the new equipment integrates seamlessly into the production environment.
Types of CNC Machining Centers: Finding the Right Fit
Businesses choose from various CNC machining center types. Each type offers distinct advantages for specific manufacturing needs. Understanding these differences helps companies select the best machine for their operations.
Vertical Machining Centers (VMCs)
Vertical Machining Centers (VMCs) are a common choice in many industries. They offer high precision and efficiency. VMCs produce intricate parts and perform complex tasks with minimal material waste. They reduce labor costs and increase output, providing financial benefits. VMCs handle both high-volume and custom production easily. They feature advanced spindle technologies and rigid tool-holding systems. This ensures high-quality results for demanding projects. Many VMCs include robotic tool changers and adaptive machining. This reduces human intervention and boosts productivity. High-speed spindles allow VMCs to work with diverse materials. These materials range from soft metals to hard alloys, shortening processing times. Modern VMCs offer real-time data monitoring and IoT connectivity. This enables them to detect abnormalities and predict maintenance. VMCs find use in aerospace, automotive, renewable energy, medical, and agriculture industries.
Horizontal Machining Centers (HMCs)
Horizontal Machining Centers (HMCs) offer significant productivity advantages. They excel in applications like aerospace, automotive, and die and mold making. HMCs provide precision, cost-effectiveness, and versatility. They feature excellent thermal stability and reduce setup time. HMCs also extend tool life and offer efficient chip evacuation. Automatic tool changing and multi-axis capability enhance their performance. One HMC can replace three VMCs. This reduces the need for multiple operators and saves floor space. HMCs offer greater automation capabilities. These include multiple pallet changing and larger tool storage. Their increased productivity leads to a faster return on investment.
5-Axis CNC Machining Centers
5-Axis CNC Machining Centers provide advanced capabilities for complex parts. They minimize setup time. This allows access to nearly all surfaces of a component in a single setup. This reduces manual rotations and saves time. These machines create intricate designs and shapes. They handle arcs and angles without complex fixtures. Rotational accuracy improves precision. The machine completes the entire job in one setup, maintaining alignment. Faster material removal is another benefit. The cutting tool remains tangential to the surface. This enables more material removal per pass. It leads to shorter cycle times and increased efficiency. Better surface finishes result from shorter tools. These tools vibrate less at high speeds. This reduces machining time compared to 3-axis machines. Industries like aerospace, medical device manufacturing, military, and energy equipment use 5-axis machines. They also benefit pharmaceuticals and food processing.
Multi-Tasking Machines (Mill-Turn)
Multi-tasking machines, often called mill-turn centers, combine the capabilities of both milling and turning operations into a single machine. This integration offers significant advantages for manufacturers. These machines improve work efficiency by reducing workpiece changeovers and waiting times. This shortens overall production and delivery schedules. They also help eliminate labor shortages by automating skilled operations, which reduces manpower needs and allows for continuous operation.
Mill-turn machines save valuable floor space. They consolidate multiple machines into one unit, optimizing the factory layout. This makes them ideal for high-mix, low-volume production, supporting small lot orders and improving profit margins. Many models also offer energy-saving features, contributing to a sustainable production system by reducing electricity costs and CO2 emissions.
Industries like aerospace, automotive, medical equipment, and energy sectors widely use mill-turn machines. They excel at machining complex parts with intricate geometries. Examples include engine parts, artificial joints, turbine blades, high-precision mold parts, robot arms, and watch or camera components. These machines perform various processes such as CNC turning, milling, surfacing, helical milling, 5-axis machining, hobbing, skiving, broaching, and grinding. They produce parts like surgical scissors, jet engine cases, fluid system components, and landing gear with high accuracy and repeatability.
Compact CNC Machining Centers for Small Parts
Compact CNC machining centers cater specifically to the production of small, intricate components. These machines offer high precision within a smaller footprint. Manufacturers often choose them for their ability to produce tiny, complex parts with exceptional accuracy. Industries such as medical device manufacturing, electronics, and watchmaking frequently utilize these specialized machines.
Their smaller size makes them suitable for workshops with limited space. Despite their compact design, they deliver robust performance for micro-machining tasks. These centers are cost-effective solutions for businesses focusing on high-precision, small-scale production. They ensure consistent quality for delicate components.
Key Features and Technologies for Your 2025 CNC Machining Center

Businesses must carefully evaluate the features and technologies available in modern CNC machining centers. These elements directly impact a machine’s performance, efficiency, and adaptability to future manufacturing demands. Selecting the right combination ensures optimal productivity and a competitive edge.
Spindle Speed and Power Requirements
The spindle is the heart of any CNC machining center. Its speed and power directly influence machining capabilities. High spindle speeds are crucial for efficient material removal, especially with smaller tools and harder materials. Power, measured in horsepower or kilowatts, determines the machine’s ability to cut through tough materials without bogging down. Manufacturers must match spindle specifications to their primary applications. For instance, aerospace components often require high-speed spindles for aluminum and exotic alloys, while heavy-duty mold making demands high torque at lower RPMs for steel. Consider the maximum RPM, continuous power, and peak power ratings. Also, evaluate the type of spindle, such as direct-drive or belt-driven, as this affects rigidity and vibration.
Tool Changer Capacity and Speed
An efficient tool changer significantly boosts productivity in a Cnc Machining Center. The capacity refers to the number of tools the machine can store and access automatically. A higher capacity allows for more complex operations without manual intervention. Speed, measured by tool-to-tool and chip-to-chip times, minimizes non-cutting time.
High tool changer capacity and speed offer numerous benefits:
- Increased precision in machining operations.
- Improved overall effectiveness and efficiency.
- Greater versatility for machines, allowing for a wider range of tasks.
- Fewer interruptions during production, leading to greater total production time.
- Elimination of manual operator intervention for tool changes, reducing labor costs.
- Enhanced safety for both staff and equipment.
- Increased capacity for storing a larger number of tools.
- Easier and more efficient switching for larger and heavier tools.
- Expanded tooling selection for every machining process.
Different machine types and industries particularly benefit from advanced tool changers:
| Machine Type/Industry | Benefits of High Tool Changer Capacity & Speed |
|---|---|
| Horizontal Machining Centres (HMCs) | Handle higher tool counts, run longer unattended, enable complex multi-face machining. |
| Vertical Machining Centres (VMCs) | Significantly reduce cycle times through rapid tool changes. |
| 5-axis Machining Centres | Facilitate high-speed, multi-angle tool swaps for multi-surface machining with consistent quality and optimal tool access. |
| Turn-mill and Mill-turn Machines | Maintain speed and accuracy with rapid tool transitions without spindle halts. |
| Double-column/Gantry Machines | Support long machining cycles and diverse tooling for large components and structural parts. |
| Automotive Applications | Minimize downtime between tool changes, contributing to safe, non-stop production of varied components. |
| Aerospace Applications | Enable multi-tool strategies for high-precision, lightweight components, maintaining extreme accuracy and seamless transitions. |
| Medical Applications | Ensure exact tool positioning and avoid human error for repeatability in sensitive operations. |
| Mould Die Making Applications | Offer improved tool life and smooth, vibration-free tool changing for frequent, critical tool changes. |
| Energy Applications (gas, oil, wind) | Maintain stability while handling long or large-diameter tools for complex profiles and large castings. |
These advantages underscore the importance of a robust and fast tool changer for maximizing machine utilization and throughput.
Control System (CNC Controller) Capabilities
The CNC controller acts as the brain of the machining center. It interprets G-code, manages machine movements, and oversees all operational parameters. Choosing the right CNC controller is crucial for efficient machine operation. A LinkedIn post titled ‘Top CNC Controller Brands of 2025: A Guide for Smooth Operations’ highlights this importance. This guide explores leading CNC controller brands for 2025, detailing their strengths, features, and reliability. This information helps users make informed decisions for their factories.
Leading brands offer distinct advantages:
| Brand | Key Features (2025) | Notable Aspects |
|---|---|---|
| Mazak (INTEGREX series) | Innovation in multi-axis machining | Leading player in CNC market, used in aerospace, automotive, precision engineering |
| DMG MORI (NHX Series) | Advanced control systems, digital twins, IoT integration for operational efficiency | Robust market presence, advancements in 5-axis and 6-axis machining, used in automotive, general machinery, mass production |
| Haas Automation (VF Series) | Enhanced software for better precision, integration with Industry 4.0 technologies | Versatility, affordability, reliability, popular for SMEs in general machining, electronics, small-scale production |
| FANUC (Robodrill Series) | Advanced CNC controls, AI-driven automation, real-time monitoring, IoT integration | Top-tier CNC manufacturer, celebrated for precision, used in electronics, medical devices, semiconductors |
Key trends influence CNC machines and their control systems for 2025:
- Multi-Axis Machining: The increasing adoption of 5-axis and 6-axis CNC machines for enhanced precision and efficiency in complex part production.
- Integration of AI and IoT: Manufacturers are incorporating AI, machine learning, and IoT for real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and digital twins, aiming to reduce downtime and errors.
- Sustainability and Efficiency: New CNC machines are designed to lower operational costs and energy consumption, aligning with environmental goals.
- Additive Manufacturing Integration: The growing combination of CNC with 3D printing technologies to offer multi-material capabilities and reduce waste.
- Demand in Emerging Markets: Significant growth in the CNC market, particularly in the Asia-Pacific region, driven by government initiatives and rapid industrialization.
These trends indicate a shift towards more intelligent, connected, and efficient control systems. Businesses should prioritize controllers offering advanced features like conversational programming, remote diagnostics, and seamless integration with CAD/CAM software.
Automation and Robotics Integration
Modern manufacturing increasingly relies on automation and robotics to enhance efficiency and address labor challenges. Integrating these technologies into a Cnc Machining Center transforms production capabilities. Businesses can achieve higher throughput, consistent quality, and greater operational flexibility.
Collaborative robots, known as cobots, are becoming more common. They operate safely alongside human workers without needing protective cages. This reduces setup requirements and makes automation accessible to more businesses. Cobots are flexible; workers can quickly re-task them for various operations. These tasks include loading materials or inspecting parts. Their intuitive programming helps address labor shortages by handling manual tasks. This frees skilled machinists for more complex responsibilities.
Lights-out manufacturing is also gaining traction. This approach involves fully automated operations running without human intervention, often 24/7. It significantly boosts throughput and lowers labor costs. Advanced tool management, robust part handling systems like automated pallet systems and robotic arms, and smart sensors enable this. IoT integration provides continuous data feedback and remote alerts. This can double or triple output without increasing staff, leading to higher profit margins and shorter lead times.
Artificial intelligence (AI) plays a crucial role in process optimization. AI is used for intelligent CAM programming. It suggests optimal toolpaths, feeds, and speeds based on historical data. Machine learning algorithms predict wear patterns. They adapt strategies for consistent part quality. AI also enables predictive maintenance. It analyzes sensor data to foresee failures, minimizing downtime and extending machine life. This allows CNC shops to adapt to new job requirements and reduce unplanned outages. AI also makes CNC robotics more accessible and efficient. Simplified robot programming lowers the learning curve. Operators with minimal technical expertise can implement and manage robotic systems.
Automated inspection and quality control improve product reliability. Robots with touch probes or 3D laser scanners automate first-article and in-process inspection. They measure parts for dimensional accuracy directly on the shop floor, reducing bottlenecks. Advanced setups integrate inspection data for real-time correction loops. They automatically adjust tool offsets to achieve near-zero scrap rates. This preserves quality even with increased production speeds and part complexities.
Mobile robotics streamline material handling. Autonomous Guided Vehicles (AGVs) and Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) shuttle raw stock, tooling, or finished goods. This allows employees to focus on higher-value tasks. These robots offer flexible shop floor layouts. They reduce the need for fixed conveyor systems and simplify route reconfiguration. This increases agility, cuts idle machine time, and maintains continuous throughput with minimal labor.
Cloud and edge computing connect CNC machines and robots. They send operational data to cloud-based dashboards. Edge computing preprocesses data on-site for immediate decisions. The cloud handles overarching analytics. This enables distributed workflows. Engineers can monitor production and receive alerts remotely. Vendors can offer remote updates. This ensures tight synchronization, boosting responsiveness and machine usage rates.
Simulation and digital twins offer significant advantages. Shops use simulated models, or digital twins, of layouts and operations for virtual commissioning. This identifies inefficiencies, collision risks, or bottlenecks before physical integration. Live digital twins, updated by sensor data, help planners detect and solve problems virtually. They customize workflows for new orders. This avoids expensive trial-and-error, accelerating deployment and maximizing ROI.
Robotics also enhance safety and workforce synergy. Robots handle repetitive or awkward motions, improving safety records and employee morale. This leads to higher productivity, quality improvements, and continuous technological advancement through a well-coordinated human-robot workforce. Employee roles are evolving to focus on high-value tasks and technical operations.
Connectivity and Industry 4.0 Readiness
Industry 4.0 readiness is essential for modern CNC machining centers. It transforms traditional manufacturing into intelligent, connected systems. This significantly impacts efficiency and data utilization.
IoT integration allows real-time monitoring and data analysis from sensors. This provides insights into machine performance. It enables immediate adjustments and enhances control, reducing errors and increasing output quality. Predictive maintenance, enabled by IoT and machine learning, analyzes data trends. It forecasts potential machine failures, minimizing unexpected downtime and improving maintenance accuracy.
Enhanced precision and automation are achieved as IoT systems feed data back to CNC machines. This allows self-regulation for optimal performance and reduces human intervention. Industry 4.0 transforms CNC machines into intelligent systems. They are capable of self-optimization and decision-making within a connected manufacturing ecosystem.
Integration with AI, robotics, and additive manufacturing enhances CNC capabilities. This leads to more efficient operations, streamlined workflows, and flexible design possibilities. Manufacturing workflows become more agile. They support rapid prototyping and dynamic responses to market demands. This shifts from linear to flexible, modular, and scalable approaches.
Increased productivity and efficiency result from IoT-driven CNC machines. They operate at optimal speeds, manage resources efficiently, and reduce batch switchover times. Preemptive issue identification prevents downtime. This also leads to a reduction in downtime and operational costs. IoT-enabled predictive maintenance prevents breakdowns and lowers expenses associated with machine failure and servicing.
Customization and flexibility are enhanced. IoT-equipped CNC machines can quickly adjust to new specifications. This enables manufacturers to offer a wider range of tailored products without sacrificing efficiency. Industry 4.0 also enables better utilization of resources and cost reduction in CNC manufacturing. Adaptive manufacturing increases flexibility in production processes. It allows adjustment to changing demands.
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability Features
The focus on energy efficiency and sustainability continues to grow in manufacturing. Modern CNC machining centers incorporate features that reduce environmental impact and operational costs. Businesses prioritize machines that meet stringent energy consumption benchmarks.
The ERP Directive 2023 mandates that compliant CNC machines must meet specific kW/hr benchmarks across various operational states. Facility audits verify compliance. These CE-compliant machines typically offer 25-35% lower energy consumption compared to older models.
The following table illustrates energy consumption benchmarks for different CNC machine types and operation modes:
| CNC Machine Type and Operation Mode | DMG MORI Ecoline (kW/hr) | Industry Average (kW/hr) | Conventional (kW/hr) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3-Axis Milling | 5.6 | 9.0 | 11.3 |
| 5-Axis Milling | 8.5 | 13.0 | 15.8 |
| Turning | 4.5 | 6.8 | 9.0 |
| Standby Mode | 0.8 | 2.4 | 3.0 |
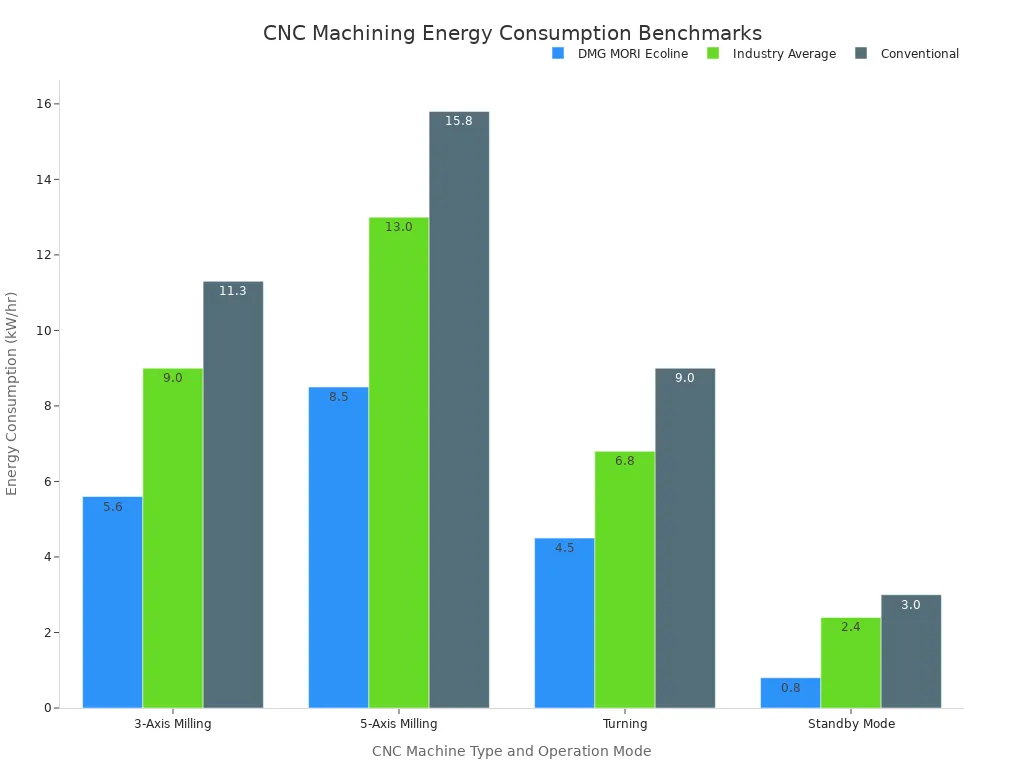
These benchmarks highlight the significant energy savings achievable with modern, eco-friendly machines. Operating more sustainably is a growing push. This is driven by environmental concerns and the desire for operational efficiency. Automation, such as automated deburring, contributes to sustainability. It optimizes processes and reduces waste. Manufacturers are also exploring integrating additive manufacturing (3D printing) for enhanced capabilities and reduced material waste.
Assessing Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) and ROI for a CNC Machining Center
Businesses must look beyond the initial purchase price when acquiring new equipment. They need to evaluate the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) and potential Return on Investment (ROI). TCO encompasses all expenses associated with a machine throughout its operational life. A thorough TCO analysis helps businesses make financially sound decisions. It ensures the chosen equipment provides long-term value and profitability.
Initial Purchase Price vs. Long-Term Value
The initial purchase price often captures immediate attention. However, it represents only one component of a machine’s true cost. Businesses must consider the long-term value a machine offers. This includes its durability, efficiency, and advanced features. A higher initial investment in a quality machine often leads to lower operating costs and greater productivity over time.
The initial purchase price for a new machine varies significantly based on its type and capabilities.
| Machine Type | China Price Range | USA Price Range |
|---|---|---|
| Vertical Machining Center | $45,000-$120,000 | $75,000-$180,000 |
| 5-Axis Machine | $150,000-$350,000 | $220,000-$500,000 |
More generally, prices for milling machines break down as follows:
- Entry/hobby mills: $3,000–$4,000
- Mid/pro mills (3–4 axis): $30,000–$100,000
- Industrial mills: $100,000–$500,000+
- 5-Axis Machining Center (Mid/Pro Range): $150,000–$300,000
- 5-Axis Machining Center (Industrial Range): $300,000–$500,000+
Investing in a higher-priced machine with superior technology often yields greater long-term value. These machines offer better precision, faster production, and reduced downtime. They also typically have a longer operational life. This translates into higher productivity and profitability over many years.
Operating Costs and Consumables
Operating costs represent a substantial portion of a machine’s TCO. These expenses include energy consumption, tooling, coolants, and software licenses. Businesses must budget for these ongoing costs. Neglecting them can lead to unexpected financial strain.
Annual ownership costs vary by machine type:
| CNC Machine Type | Annual Ownership Cost |
|---|---|
| Mid-range three-axis VMC | ~$24,700 (includes software, maintenance, consumable tooling, energy, insurance) |
| Desktop CNC router | ~$8,000 |
| Fiber laser | ~$35,000 |
Software costs also add to the annual expenses. Annual software costs typically range from $2,000 to $15,000. Consumables like cutters and coolants require regular replenishment.
| Consumable | Monthly Cost |
|---|---|
| Cutters | ~$6,000 |
| Coolant | ~$1,200 per drum |
Efficient machines consume less energy. They also use consumables more effectively. This reduces daily operational expenses. Businesses should factor these recurring costs into their financial planning.
Maintenance and Service Agreements
Maintenance costs significantly impact a machine’s TCO. Regular servicing prevents unexpected breakdowns and extends machine life. Businesses must plan for both routine maintenance and potential repair expenses. Proactive maintenance strategies minimize costly downtime.
Annual maintenance costs for CNC lathes typically range from $1,000 to $5,000 for routine servicing. Consumables and software updates can add an estimated 10–25% to the total operating costs. Repair costs for components like controllers, servo motors, and sensors can range from $1,000 to $10,000 each.
Service agreements offer several benefits. They provide peace of mind and help manage maintenance budgets.
- 24/7 Technical Support: This expedites issue resolution. It also offers expert remote diagnostics.
- Scheduled Maintenance: Proactive service visits coordinate with production schedules.
- Priority Parts Access: On-site inventory of critical spare parts ensures faster repairs.
These agreements help minimize downtime. They ensure machines operate at peak performance. Choosing a reliable service provider is crucial for long-term machine health.
Resale Value and Depreciation
Depreciation refers to the decrease in an asset’s value over time. CNC machines, like other capital equipment, lose value due to age, wear, and technological advancements. Businesses must understand depreciation when planning for future equipment upgrades or sales.
Several factors influence a CNC machine’s resale value. Machine condition plays a significant role. Well-maintained machines with complete service records command higher prices. Brand reputation also impacts resale value. Established manufacturers often retain value better than lesser-known brands.
Technological obsolescence is another key factor. Rapid advancements in CNC technology can quickly reduce the value of older models. Machines with outdated control systems or limited automation features may depreciate faster. Market demand for specific machine types also affects resale value. High-demand models hold their value more effectively.
Businesses can implement strategies to maximize resale value. Regular preventative maintenance extends machine life and preserves condition. Keeping detailed maintenance logs provides proof of care. Strategic upgrades, such as control system updates or automation additions, can also enhance a machine’s appeal. Considering resale value during the initial purchase helps businesses plan for the machine’s entire lifecycle.
Calculating Return on Investment (ROI)
Calculating Return on Investment (ROI) provides a critical metric for evaluating a machine purchase. ROI measures the financial benefit of an investment relative to its cost. Businesses use ROI to justify capital expenditures and compare different investment opportunities.
The basic ROI formula is: (Net Profit from Investment / Cost of Investment) x 100%.
For a machine, “Net Profit from Investment” includes all financial gains. These gains come from increased production capacity, reduced labor costs, and improved part quality. It also includes savings from less scrap material and new revenue streams from expanded capabilities. “Cost of Investment” encompasses the initial purchase price, installation, training, and ongoing operating expenses. These expenses include maintenance, consumables, and software.
A comprehensive ROI analysis requires careful estimation of both benefits and costs over the machine’s expected lifespan. For example, a new machine might increase production by 20% and reduce scrap by 5%. These improvements directly contribute to net profit. Simultaneously, the machine’s energy consumption and maintenance needs add to the cost.
Businesses should also consider qualitative benefits. These benefits are harder to quantify but still contribute to overall value. Examples include enhanced employee morale due to modern equipment, improved market reputation from higher quality products, and greater flexibility in production scheduling. A positive ROI indicates a financially sound investment. It shows the machine will generate more value than its cost over time. This calculation helps businesses make informed decisions. It ensures the investment aligns with financial goals and operational objectives.
Selecting the Right Vendor for Your CNC Machining Center
Businesses must carefully choose a vendor for their new Cnc Machining Center. This decision significantly impacts long-term operational success. A thorough evaluation of potential suppliers ensures a reliable partnership.
Vendor Reputation and Reliability
A reputable vendor demonstrates extensive expertise and experience. They possess deep knowledge in material proficiency, handling specific materials like aerospace-grade titanium, plastics, or exotic alloys. They also show capabilities with intricate part complexity, tight tolerances, and multi-axis machining. Industry-specific knowledge, including relevant certifications such as ISO or AS9100, is also important.
Vendors should utilize modern equipment and technology. This includes various CNC machines, high-speed spindles, and advanced controls. They maintain rigorous maintenance schedules and calibration procedures for consistent performance. Quality control is crucial. Reputable vendors use advanced inspection tools like Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMMs) and hold ISO 9001 certification. They ensure on-time delivery through advanced planning systems. Proactive communication is a hallmark of reliable suppliers. They confirm purchase orders, provide estimated timelines, and alert customers to potential issues before delays occur.
Technical Support and Training Offerings
Excellent technical support and comprehensive training programs are essential for maximizing machine utility. Vendors should offer various services to ensure smooth machine operation. These include CNC technical repair and maintenance training. Applications training helps operators maximize machine capabilities. EDM training is available for specialized processes. Vendors provide service and preventative maintenance. They also handle parts requests efficiently. Automation solutions, servo tuning, and pitch-error compensation are often part of their offerings. They perform level and square alignment, along with ballbar circularity inspection and tram testing.
Parts Availability and Warranty
Businesses must consider parts availability and warranty terms. A strong warranty protects the investment. NS CNC Manufacturing Limited provides a 12-month warranty for new milling machines and their components. This covers defects in material and craftsmanship from the delivery date. Shibaura Machine offers a 12-month warranty for manufactured parts, circuit boards, and electric components. This warranty starts on the machine’s start-up date or 60 days from the invoice. STYLECNC also offers at least a one-year warranty for new CNC machines and their parts. Warranted parts are typically expedited and shipped prepaid for next-day delivery, subject to availability. This ensures minimal downtime.
Customization Options for Your CNC Machining Center
Businesses often require tailored solutions to meet specific production needs. Customization options for a machining center allow manufacturers to optimize equipment for unique applications. This ensures the machine performs exactly as required for specialized tasks.
Manufacturers can customize machines for multi-axis machining. Options include 4-axis machining, which adds rotation around one axis. 5-axis machining incorporates two rotational axes. This allows tool approach from virtually any direction. These capabilities enable the creation of complex geometries like compound curves and undercuts. Tolerance capabilities also vary. Machines achieve standard tolerances (±0.005″) for general components. They can also reach ultra-precision (±0.0001″) for specialized instruments and optical components.
Material considerations are important for customization. This involves selecting appropriate materials that respond well to machining processes. Businesses also consider their anisotropic properties for consistent tolerances. Specialized tooling, such as extended-reach tools, and custom fixtures securely hold workpieces. They also access complex surfaces, balancing reach with rigidity. Advanced CAM software and progressive machining strategies optimize precision and surface finish. These strategies include roughing, semi-finishing, finishing passes, and on-machine probing for complex geometries.
A wide range of finishes can be applied:
- Mechanical Finishes: This includes polishing (standard, fine, mirror), brushing, and vibratory finishing.
- Chemical Finishes: Examples are anodizing (Type I, II, III) for aluminum, chemical film (passivation) for stainless steel, and electroplating (nickel, chrome, zinc, gold).
- Coating-Based Finishes: These include powder coating and painting/clear coating for durability, chemical resistance, and aesthetic variety.
These customization options ensure the machine perfectly aligns with production demands. This leads to improved efficiency and product quality.
Post-Purchase Considerations for Your New CNC Machining Center
Acquiring a new Cnc Machining Center marks a significant investment. However, the journey does not end with the purchase. Businesses must carefully plan for post-purchase activities. These steps ensure optimal performance, longevity, and a strong return on investment.
Site Preparation and Installation
Proper site preparation and installation are crucial for machine performance. Businesses must consider the machine’s layout. This includes door clearance, proximity to walls, and accessibility for maintenance. The concrete floor must be sufficiently thick. The machine needs a solid slab to ensure accurate cutting. Controlling shop humidity prevents premature rust inside the machine tool. This protects performance. Businesses must have all necessary fluids ready. These include lubricating oil, coolant, and hydraulic oil. They must ensure the correct types to avoid equipment damage.
Key installation steps involve selecting an appropriate site. This site should be free from direct sunlight and far from heat sources. It needs low dust concentration. The equipment foundation must be solid and stable. Vibration isolation measures are necessary if strong vibration sources are nearby. Equipment fixing involves placing the machine directly on the foundation or concrete floor. Anchor bolts firmly fix it to ensure stability. After installation, businesses must clean anti-rust oil from the equipment surface. They then apply a layer of machine oil to prevent corrosion. Critical infrastructure requirements include a stable power system. This system needs dedicated electrical circuits and proper surge protection. Air supply requires a minimum 100 PSI capacity and professional-grade filtration.
Operator Training and Skill Development
Investing in operator training and skill development is vital. Well-trained personnel maximize machine capabilities and ensure safe operation. Santa Ana College offers a Certificate of Achievement in Manufacturing Technology Computer Numerical Control Programmer A (Mastercam). This program covers essential skills. Required courses include Basic Mechanical Blueprint Reading, Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing, and Technical Mathematics. Students also learn Basic Machining Concepts and Operation, CNC Program Writing, and Manufacturing Technology Lab. Mastercam courses cover 2D Geometry, 2D Toolpaths, 3D Geometry, 3D Surfaces, 3D Toolpath, CAM Applications, Lathe, and 5 Axis Mill Toolpath.
Online resources also provide valuable training. GCodeTutor offers professional G-Code training courses. These cover G-Code programming for milling machines, lathes, and machining centers. Individual courses include Foundation G Code, CNC Lathe Programming, CNC Mill Programming, and Advanced CNC macro programming. Bundles are available, such as the 4-course G-Code bundle. The Everything Bundle includes G-Code, Fusion 360 CAD/CAM, Machine Shop Maths, GD&T, and Manual Lathe courses. Free introductory courses are also offered.
Software Integration and CAM Programming
Effective software integration and CAM programming unlock a machine’s full potential. Businesses should start with fundamental features. They then move to advanced capabilities. Mastering basics like toolpath creation and G-code generation is essential. Investing time in setting up tooling libraries properly leads to faster setup times and consistent results. Utilizing digital twin capabilities and simulation tools helps. These tools virtually test and refine programs. This saves time and materials. Businesses should begin with simple projects. They can gradually increase complexity. Taking advantage of available training resources, including professional training, is beneficial. Keeping tooling libraries updated with current information ensures accuracy. Regularly exploring new features helps skills develop.
Ongoing Support and Preventative Maintenance
Ongoing support and preventative maintenance are crucial for a machine’s long-term performance. These practices ensure the equipment operates efficiently and reliably. They also extend the machine’s lifespan. Businesses must implement a robust maintenance schedule. This proactive approach minimizes unexpected downtime and costly repairs.
Daily maintenance tasks keep machines running smoothly. Operators check and replenish lubrication levels. They grease dry parts. They also check coolant concentration and fill levels. Emptying the chip hopper is another daily task. Operators check hydraulic system levels. They wipe down all surfaces to prevent metal shaving buildup.
Monthly maintenance involves more detailed checks. Workers clean or replace air filters. They check and clean coolant filters. They also clean radiators and cooling fans. Reviewing oil fill checklists for unusual oil consumption is important. Removing and cleaning chuck and jaws is necessary. Greasing and adjusting chains or conveyors also occur monthly.
Semi-yearly tasks include lubricating all moving parts. Technicians check and calibrate the machine’s accuracy and precision. They inspect and thoroughly clean the coolant system. Examining and tightening all bolts and fasteners is vital. Cleaning and inspecting the machine’s electrical components also happens. Testing and verifying emergency stop and safety systems ensures safety.
Yearly maintenance involves comprehensive checks. Mechanically, technicians check radial and axial play of the spindle for proper alignment. They replace all guideway wipers. They inspect guideway mounting for stability and alignment. They evaluate bearing condition. They check and align machine base leveling. They check the headstock for tapering. They inspect and adjust drawbar tension. They run a backlash program and replace X and Y axis gibs if needed. Electrically, they inspect and tighten all electrical connections and terminals. They check and test the machine’s electrical grounding system. They verify proper functioning of all control panel components. They clean and inspect the machine’s electrical cabinet. Hydraulically, they drain and replace hydraulic oil and filters. They test hydraulic oil for contaminants and replace filters as needed. They inspect and test hydraulic pumps and valves. They check and replace hydraulic hoses if necessary. Additional yearly tasks include removing and cleaning the coolant tank. They drain and clean the lubrication unit. They perform a comprehensive cleaning of the entire machine. They calibrate the machine’s accuracy and precision. They test and verify emergency stop and safety systems. They inspect and replace worn or damaged belts. They lubricate all moving parts and ball screws. They inspect the chuck cylinder for proper operation. They review and update the maintenance schedule based on performance.
Making an informed decision on a Cnc Machining Center in 2025 is crucial for long-term success. Businesses must carefully consider their specific operational needs. They should evaluate all available technologies. Assessing financial implications is also vital for planning. A strategic investment will drive productivity. It will foster innovation. This leads to sustained growth for the company.
FAQ
What is the most important factor when choosing a CNC machining center?
Businesses must first understand their specific operational needs. This includes current and projected production volume, material types, and part complexity. This foundational assessment ensures the chosen machine aligns with business goals and maximizes return on investment.
What are the key differences between VMCs and HMCs?
Vertical Machining Centers (VMCs) typically have a vertical spindle. They excel at precision work on one side of a part. Horizontal Machining Centers (HMCs) feature a horizontal spindle. They offer greater automation and multi-face machining capabilities, often replacing multiple VMCs.
Why should businesses consider a 5-axis CNC machining center?
A 5-axis CNC machining center minimizes setup time. It accesses nearly all part surfaces in one setup. This reduces manual rotations and creates intricate designs. It also allows faster material removal and achieves better surface finishes for complex components.
What does Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) include for a CNC machine?
TCO includes the initial purchase price, operating costs like energy and consumables, and maintenance expenses. It also accounts for service agreements, resale value, and depreciation. Businesses evaluate TCO to understand the machine’s full financial impact over its lifespan.
Post time: Dec-22-2025







